Part:BBa_K404127
[AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_mVenus_[AAV2]-right-ITR
Usage and Biology
| [AAV2-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_mVenus_[AAV2]-right-ITR] | |
|---|---|
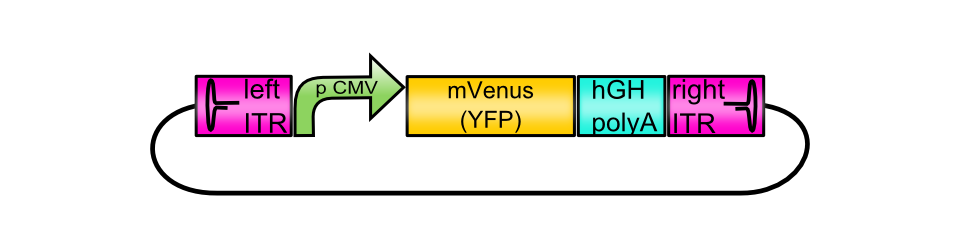
| |
| BioBrick Nr. | BBa_K404127 |
| RFC standard | RFC 10 |
| Requirement | pSB1C3 |
| Source | Assembled vectorplasmid of provided BioBricks |
| Submitted by | [http://2010.igem.org/Team:Freiburg_Bioware FreiGEM 2010] |
The iGEM team Freiburg provides an hGH plolyadenylation sequence within the ‘Virus Construction Kit’ due to the fact that almost every eukaryotic mRNA is processed at their 3´ and 5´end except for histone mRNAs (Millevoi et al. 2006). Pre-mRNAs contain two canonical conserved sequences. First, the polyadenylation signal “AATAAA” which is recognized by the multiprotein complex and second the GT-rich region (downstream sequence element, DSE) which is located 30 nucleotides downstream of the cleavage site. The assembled 3´end-processing machinery cleaves the mRNA transcript immediately after a CA-nucleotide therefore defining the cleavage site (Danckwardt et al. 2008).
 Figure 1: Assembled vectorplasmid missing the hGH termination signal..
Figure 1: Assembled vectorplasmid missing the hGH termination signal..
Characterization
Recombinant AAV genomes were engineered containing the inverted terminal repeats (ITRs), a strong eukaryotic promoter and mVenus as gene of interest with and without the hGH terminator signal. Transduction of HT1080 cells with viral particles containing the rAAV genomes and measuring mVenus expression 24-hours post infection by flow cytometry demonstrated that transgene expression of the constructs lacking the hGH termination signal is significantly reduced. Therefore, the expected result that hGH is essential for mRNA processing could be confirmed. The iGEM team Freiburg_Bioware 2010 therefore suggests using the provided hGH termination signal within the Virus Construction Kit for optimal gene expression.
References
Danckwardt, S., Hentze, M.W. & Kulozik, A.E., 2008. 3' end mRNA processing: molecular mechanisms and implications for health and disease. The EMBO journal, 27(3), 482-98. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18256699.
Millevoi, S. et al., 2006. An interaction between U2AF 65 and CF I(m) links the splicing and 3' end processing machineries. The EMBO journal, 25(20), 4854-64. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17024186.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1319
Illegal AgeI site found at 2039 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
//viral_vectors
//viral_vectors/aav
//viral_vectors/aav/vector_plasmid
| None |
